“아, 이건 기록을 안 해뒀네…” 하면서 그냥 잊으려 했는데, 메모를 정리하다가 발견해버렸다. ㅠ.ㅠ Elastic Stack으로 NetFlow와 SNMP 모니터링을 구성했던 이야기. NMS라고 하면서 SNMP와 NetFlow를 빼면 좀 섭하지… 했다가, 귀찮지만 닫았던 묶음글을 다시 열어서 마지막으로 이번 이야기, NetFlow와 SNMP 모니터링 하기를 더 넣는다. 이번엔 SNMP로 정말 끝!
이번 묶음글은 아래와 같은 순으로 진행할 예정이다. 깊이있게 다루는 것은 아니며, Elastic Stack을 시작하는 입장에서 관심있는 부분을 참고하면 될 것 같다.
"Elastic NMS" 묶음글은 다음과 같습니다.
이 묶음글과 직접적인 관련은 없지만, 혹시 로그중앙화를 위한 간편한 솔루션을 찾는다면 이보다 앞서 검토했던 Graylog2에 대해 정리했던 글이 더욱 도움이 될 수도 있다. Graylog2는 로그중앙화와 검색, 경보발생 등이 가능한 매우 쉽고 잘 만들어진 도구다.
"Calling All Logs" 묶음글은 다음과 같습니다.
NetFlow와 SNMP
네트워크 모니터링을 얘기할 때, SNMP와 NetFlow는 따로 얘기할 필요가 없을 정도로 잘 알려진 관리용 프로토콜이다. 이 시험환경에서는 각 포트, 그러니까 네트워크 연결 단위의 성능측정을 위해 SNMP를 활용하여 Count 데이터를 모아 분석하고, 개별 서버나 서비스 단위의 성능측정 등을 위해 NetFlow를 활용한 데이터를 모아 분석할 수 있도록 구성해봤다.
SNMP 모니터링 구성하기
앞서 설명했던 NetFlow와 유사한 방식으로 SNMP의 기본 설정을 만들었다.
/etc/logstash/conf.d/30-snmp.conf
input {
udp {
type => snmp
tags => [ "no_default_out", "_debug" ]
port => "7450"
codec => json_lines
add_field => { "received_at" => "%{@timestamp}" }
}
}
filter {
if [type] == "snmp" {
date {
match => [ "timestamp", "ISO8601" ]
}
mutate {
add_field => { "proxy" => "%{host}" }
}
}
}
output {
if [type] == "snmp" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["127.0.0.1"]
index => "snmp-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
앞선 syslog나 NetFlow와는 조금 다른 접근방법을 사용한 부분은, syslog 나 NetFlow의 경우, 해당 장비에서 데이터를 전송할 기계를 설정하고 이 분석용 환경에서는 단지 그것을 수신할 포트를 열어주는 방식으로 진행했었는데, SNMP는 원래 “수동적으로 긁어가는 기계에서 자료를 주는 방식"으로 설계된 것이다 보니 중간에 긁어줄 녀석을 준비해야 했다. (이 부분은 좀 얘기가 길어지므로 이 글에서는 생략한다.)
아무튼, 간략하게 Ruby로 SNMP Poller를 하나 만들었고, 그것이 위와 같이
설정한 Logstash의 7450 포트에 json 포맷의 텍스트를 밀어넣어 주도록
구성을 했다. (이 Poller 얘기는 다음에 시간이 되면 하기로…)
Mapping 해주기
아무튼, 이 Poller는 json 형식으로 데이터를 쏴주고, 그 데이터를 다시 아래와 같은 Template을 적용한 인덱스에 저장해 주었다. (이제 Template 또는 Mapping 얘기는 여러번 나왔으니까 생략)
{
"template" : "snmp-*",
"settings": {
"index.refresh_interval": "5s"
},
"mappings" : {
"_default_" : {
"_all" : {"enabled" : false},
"properties" : {
"host": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "string" },
"device": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "string" },
"ifname": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "string" },
"ifindex": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "integer" },
"ifdescr": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "string" },
"iftype": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "integer" },
"ifmtu": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "integer" },
"ifphysaddress": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "string" },
"ifadminstatus": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "integer" },
"ifoperstatus": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "integer" },
"iflastchange": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "date" },
"ifinoctets": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "long" },
"ifinerrors": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "long" },
"ifoutoctets": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "long" },
"ifouterrors": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "long" },
"ifspeed": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "integer" },
"rx_bytes": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "long" },
"tx_bytes": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "long" },
"proxy": { "index": "not_analyzed", "type": "string" }
}
}
}
}
이걸 디버깅해보면 대충 아래와 같은 값을 얻게 된다.
{
"device" => "203.0.113.90",
"timestamp" => "2016-09-13T22:36:30+09:00",
"ifindex" => 12,
"ifdescr" => "bond0.1234",
"ifinoctets" => 893098073,
"ifoutoctets" => 4150580065,
"ifspeed" => 2000000000,
"rx_bytes" => 86415,
"tx_bytes" => 146173,
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2016-09-13T13:36:30.000Z",
"type" => "snmp",
"received_at" => "2016-09-13T13:36:31.131Z",
"tags" => [
[0] "no_default_out",
[1] "_debug"
],
"host" => "127.0.0.1",
"proxy" => "127.0.0.1"
}
이제 Discover로 보면,
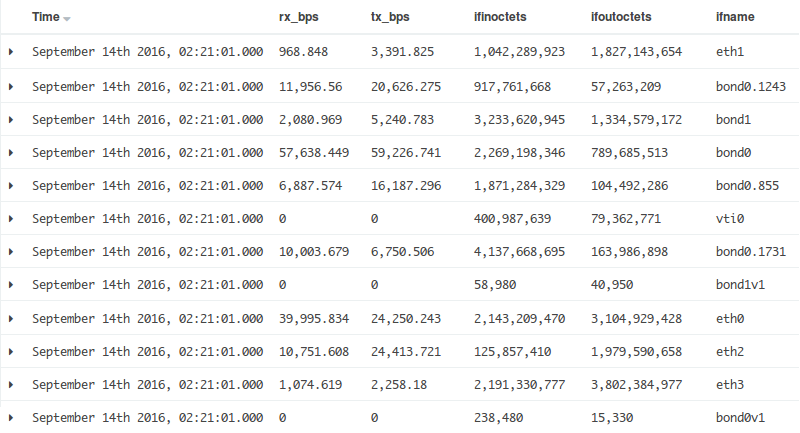
그리고 자세히 보면 아래와 같이 값과 자료형을 확인할 수 있다.
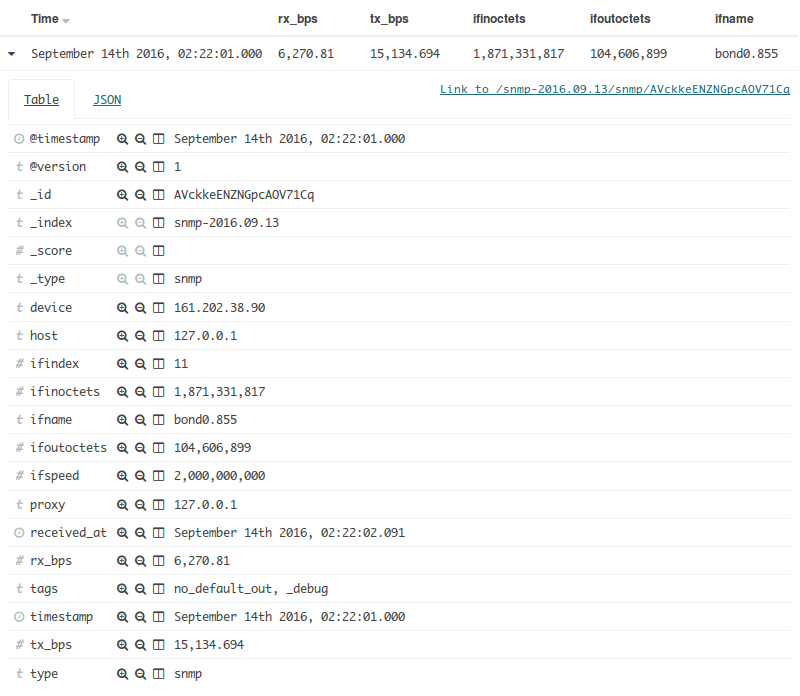
최종 설정
역시 최종적인 설정은 조금 다른데, 다음과 같다.
input {
udp {
type => snmp
port => "7450"
codec => json_lines
add_field => { "received_at" => "%{@timestamp}" }
add_field => { "[@metadata][output]" => "self" }
}
}
filter {
if [type] == "snmp" {
date {
match => [ "timestamp", "ISO8601" ]
}
mutate {
add_field => { "proxy" => "%{host}" }
}
if [device] {
mutate {
add_tag => [ "snmp" ]
add_field => { "[nms][pod]" => "%{device} pod" }
add_field => { "[nms][zone]" => "%{device} if %{ifname}" }
add_field => { "[nms][account]" => "%{device} account" }
add_field => { "[nms][hostname]" => "%{device} hostname" }
}
translate {
field => "[nms][pod]"
destination => "[nms][pod]"
override => true
dictionary_path => "/opt/hyeoncheon-elastic/conf/dict.device-map.yml"
}
translate {
field => "[nms][zone]"
destination => "[nms][zone]"
override => true
dictionary_path => "/opt/hyeoncheon-elastic/conf/dict.device-map.yml"
}
translate {
field => "[nms][account]"
destination => "[nms][account]"
override => true
dictionary_path => "/opt/hyeoncheon-elastic/conf/dict.device-map.yml"
}
translate {
field => "[nms][hostname]"
destination => "[nms][hostname]"
override => true
dictionary_path => "/opt/hyeoncheon-elastic/conf/dict.device-map.yml"
}
} else {
mutate {
add_tag => [ "ping" ]
add_field => { "[nms][pod]" => "global" }
add_field => { "[nms][zone]" => "global" }
add_field => { "[nms][account]" => "global" }
add_field => { "[nms][hostname]" => "global" }
}
}
}
}
output {
if [type] == "snmp" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["127.0.0.1"]
index => "snmp-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
NetFlow에서 설정한 내용과 유사한 구조인데, 간략히 덧붙이면 다음과 같다.
- 중간에 끼인 기계가 있으니
proxy라는 필드에 그 값을 넣어줬다. - zone, account 등의 정보는 같은 방식으로
translate하여 넣어줬다. - 전혀 설명하지 않았던 부분이긴 한데, 앞서 설명한 SNMP Poller가 하는 기능 중 하나가 주기적으로 지정된 IP에 ping 시험을 하고 그 결과를 같은 입력으로 넣어주고 있다. (이 부분은 그냥 이 글에서는 무시하시길)
Visualize해서 Dashboard에 그려보면 대충 이런 모양을 얻을 수 있다.

아무튼, 나름 쓸만하다.
묶음글, 함께 읽기 잊지 마세요!
잘못된 부분의 제보나 의견/요청 댓글 환영합니다!